Modals
With modals you can create pop-up forms that allow users to provide you with formatted inputs through submissions. We'll cover how to create, show, and receive modal forms using discord.js!
TIP
This page is a follow-up to the interactions (slash commands) page. Please carefully read that section first, so that you can understand the methods used in this section.
Building and responding with modals
Unlike message components, modals aren't strictly components themselves. They're a callback structure used to respond to interactions.
TIP
You can have a maximum of five MessageActionRows per modal, and one TextInputComponent within a row.
To create a modal you construct a new Modal. You can then use the setters to add the custom id and title.
const { Modal } = require('discord.js');
client.on('interactionCreate', async interaction => {
if (!interaction.isCommand()) return;
if (interaction.commandName === 'ping') {
const modal = new Modal()
.setCustomId('myModal')
.setTitle('My Modal');
await interaction.showModal(modal);
}
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
TIP
The custom id is a developer-defined string of up to 100 characters.
As you can see, you construct the modal and assign it a custom id and a title. After you added some user input elements, you will send it as a response to the interaction via showModal().
You are still missing one of these steps - adding inputs. Adding inputs is similar to adding components to messages.
WARNING
If you're using typescript you'll need to specify the type of components your action row holds. This can be done by specifying the generic parameter in MessageActionRow.
- new MessageActionRow()
+ new MessageActionRow<ModalActionRowComponent>()
2
const { MessageActionRow, Modal, TextInputComponent } = require('discord.js');
client.on('interactionCreate', async interaction => {
if (!interaction.isCommand()) return;
if (interaction.commandName === 'ping') {
// Create the modal
const modal = new Modal()
.setCustomId('myModal')
.setTitle('My Modal');
// Add components to modal
// Create the text input components
const favoriteColorInput = new TextInputComponent()
.setCustomId('favoriteColorInput')
// The label is the prompt the user sees for this input
.setLabel("What's your favorite color?")
// Short means only a single line of text
.setStyle('SHORT');
const hobbiesInput = new TextInputComponent()
.setCustomId('hobbiesInput')
.setLabel("What's some of your favorite hobbies?")
// Paragraph means multiple lines of text.
.setStyle('PARAGRAPH');
// An action row only holds one text input,
// so you need one action row per text input.
const firstActionRow = new MessageActionRow().addComponents(favoriteColorInput);
const secondActionRow = new MessageActionRow().addComponents(hobbiesInput);
// Add inputs to the modal
modal.addComponents(firstActionRow, secondActionRow);
// Show the modal to the user
await interaction.showModal(modal);
}
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
Restart your bot and invoke the /ping command again. You should see a popup form resembling the image below:
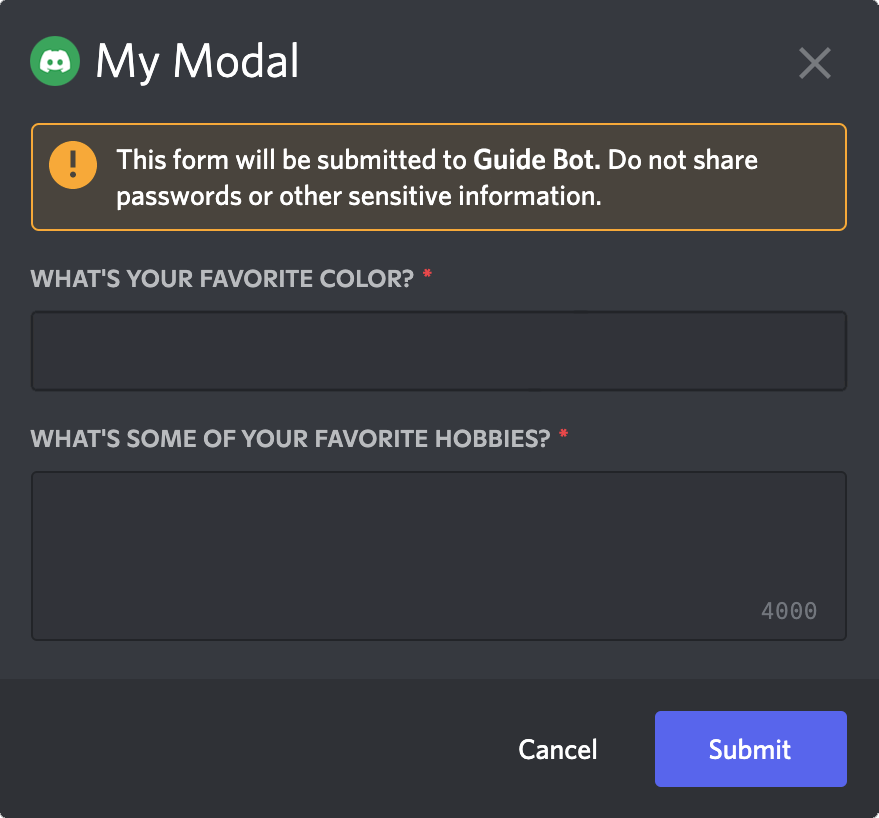
Receiving modal submissions
Modals are received via an interaction. You can check if a given interaction is a modal by invoking the #isModalSubmit() method:
client.on('interactionCreate', interaction => {
if (!interaction.isModalSubmit()) return;
console.log(interaction);
});
2
3
4
Responding to modal submissions
The ModalSubmitInteraction class provides the same methods as the CommandInteraction class. These methods behave equally:
reply()editReply()deferReply()fetchReply()deleteReply()followUp()
client.on('interactionCreate', interaction => {
if (!interaction.isModalSubmit()) return;
if (interaction.customId === 'myModal') {
await interaction.reply({ content: 'Your submission was received successfully!' });
}
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
Extracting data from modal submissions
You'll most likely need to read the data sent by the user in the modal. You can do this by accessing the fields property from the interaction. From there, you can call getTextInputValue() with the custom id of the text input to get the value.
client.on('interactionCreate', interaction => {
if (!interaction.isModalSubmit()) return;
// Get the data entered by the user
const favoriteColor = interaction.fields.getTextInputValue('favoriteColorInput');
const hobbies = interaction.fields.getTextInputValue('hobbiesInput');
console.log({ favoriteColor, hobbies });
});
2
3
4
5
6
7